Flea Allergy
What is flea allergy?
Flea allergy dermatitis (FAD) is a leading cause of allergic reactions in dogs and cats. In an allergic reaction, the body’s immune system overreacts or is hypersensitive to a substance (called an antigen) that is normally harmless.
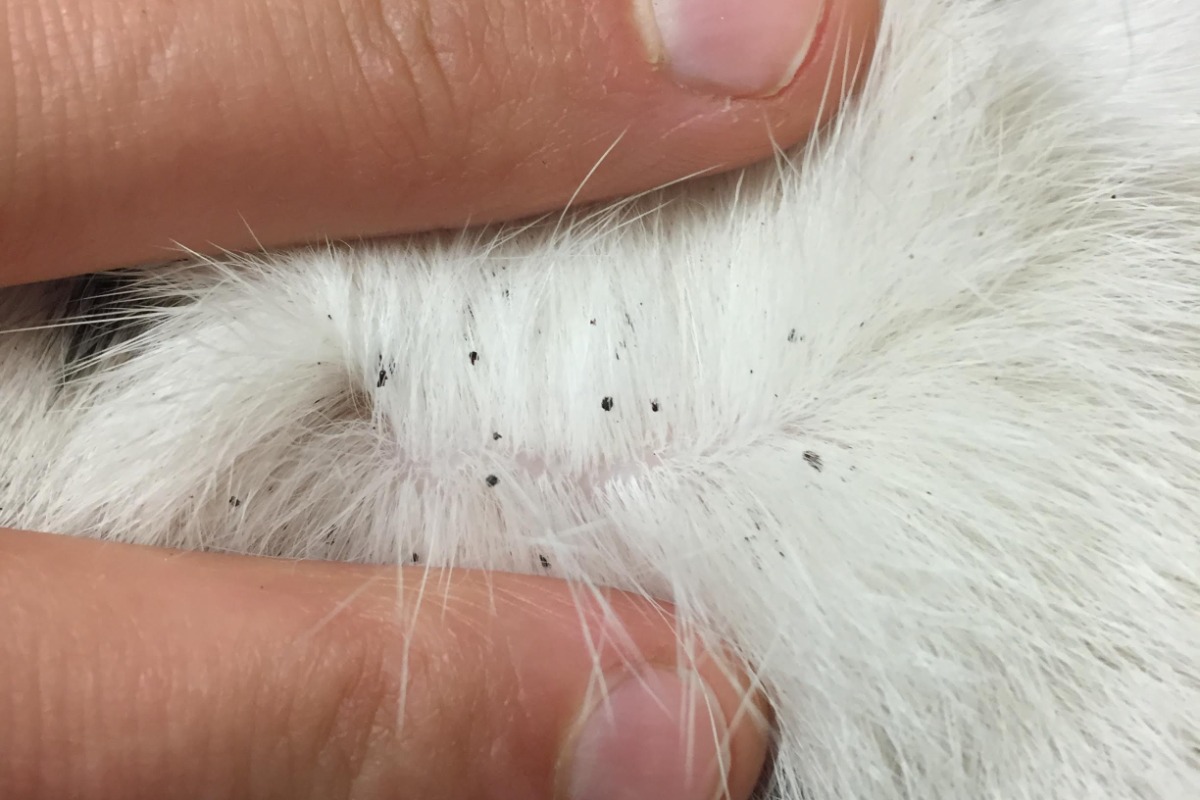
FAD is a common cause of itching in pets. Adult fleas must bite a pet and obtain a blood meal in order to reproduce. Fleas typically do not remain on the pet except for the minutes to hours when they are feeding. This is why pet owners often do not see live fleas on their pet unless there is a severe flea infestation in their immediate environment. When fleas feed, they inject a small amount of saliva into the skin. It is the antigens or proteins in the saliva that cause an intensely itchy response to sensitive dogs.
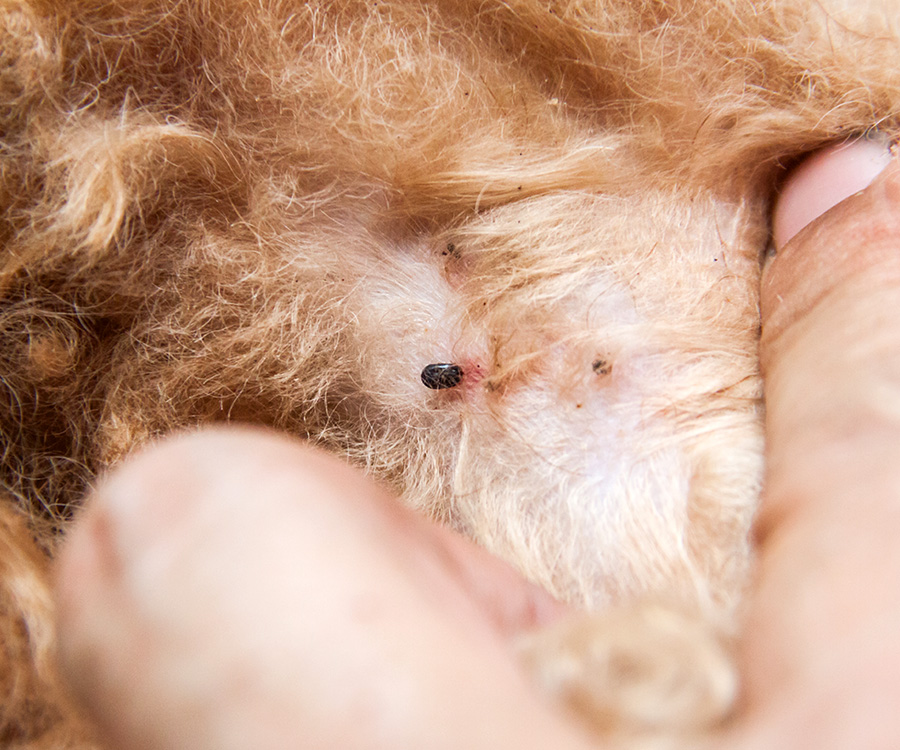

Are only certain pets allergic to fleas?
FAD can develop at any age. It is important to note that pets with other forms of allergies, such as inhaled allergies (e.g., pollens, molds, dust mites), tend to be highly sensitive to flea bites, and are therefore much more susceptible to FAD than pets that do not have other allergic conditions.
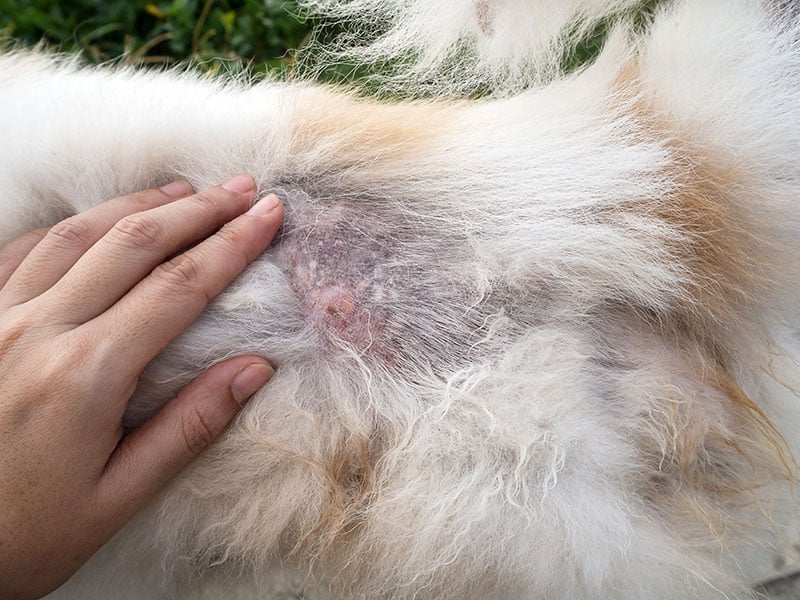
How is flea allergy dermatitis diagnosed?
Clinical signs often give the first clue that your pet may suffer from FAD. Itching and hair loss in the region from the middle of the back to the tail base and down the rear legs (the flea triangle) is often associated with FAD.
Intradermal allergy tests (skin tests similar to those performed in humans) or specialized blood tests (IgE blood tests) can confirm flea allergy in your pet. The signs of FAD are often very classic and response to treatment occurs so quickly that formal allergy testing is only necessary in some cases.




