Pemphigus Complex
Tinea is a group of five autoimmune skin diseases characterized by blisters and bullae (large and small blisters) in the oral and mucosal junction (the connection between skin and mucosal tissue). Commonly affected areas include the eyelids, lips, nostrils, and anus.
Papular urticaria (PF): The term means "foliated papules". It is the most common autoimmune skin disease in cats. Patients with PF develop crusts (scabs) and ulcers around the eyes, ears, pads, groin and nose. In cats, lesions also occur in the toenail beds, forming crusts on sore feet.PF is rarely found in the oral cavity or mucosal junctions. It usually appears suddenly and has no recognized cause, but in some cases it may be caused by medication or may be the result of years of chronic skin disease.
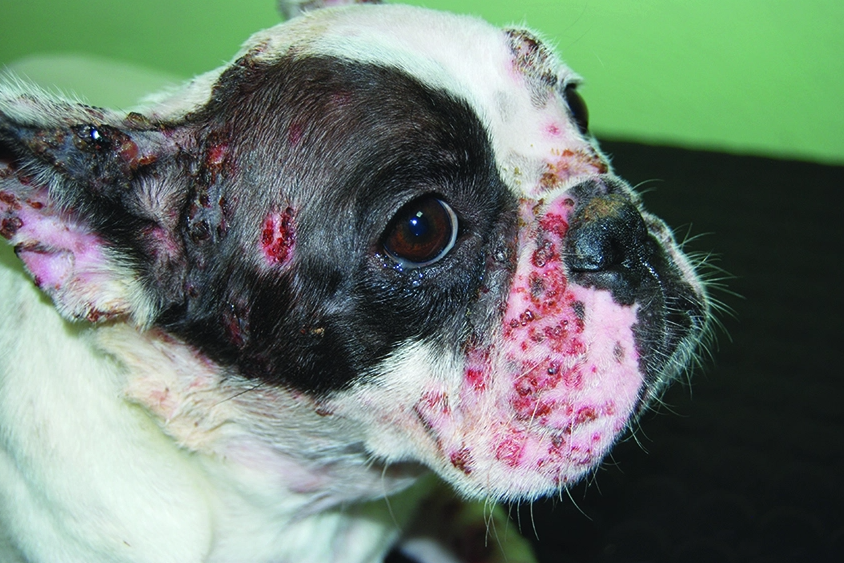
Pimples vulgaris (PV): The term means "common papulopustular dermatosis. It is the most common form of acne vulgaris in humans. Fluid-filled blisters, called blisters, form in and around the mouth, eyelids, lips, nostrils, anus, foreskin, or vulva. These blisters are prone to rupture and form painful ulcers.
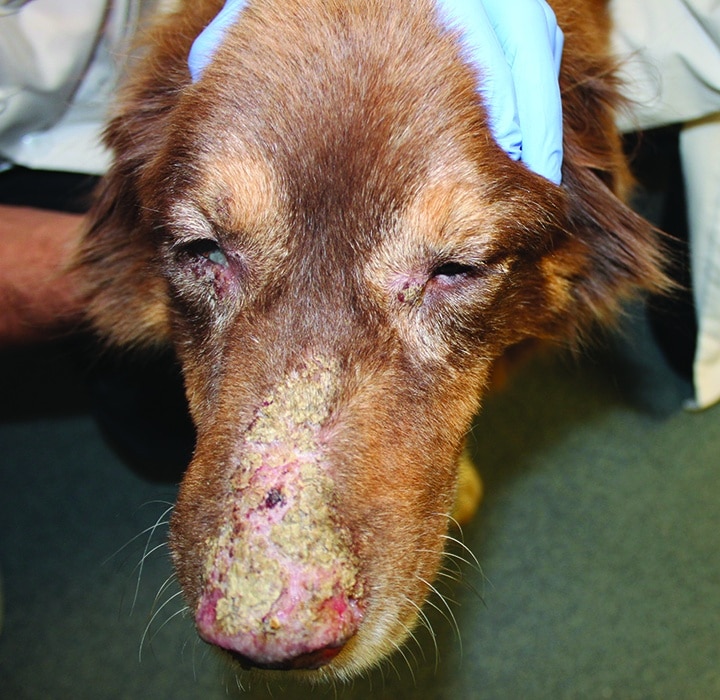
Papulopustular lupus erythematosus (PE): The term means "red and inflamed papulopustular skin disease". The most common symptoms are redness, crusting, scaling and hair loss on the nose. Exposure to ultraviolet light can make this form of papulopustular dermatosis worse.
Pustular Pustular Papules (PPP): PPP was previously classified as a vegetative papule. This form is typically characterized by thick, irregular vegetative lesions or bumps associated with chronic exudates and pustules. It is considered to be a more benign form of the unusual cold sore. To date, PPP has not been documented in cats.
Paraneoplastic papillomavirus (PNP): The least common and most severe form of papulopustular dermatosis. It is secondary to severe tumors (thymic lymphoma, splenic sarcoma).
Pemphigus Complex



